Understanding Twinaxial Cables: How Do They Differ from Coaxial Cables?
In data transmission and networking, type of cables play a role in ensuring information travels seamlessly from one point to another.
Twinaxial cables, often referred to as “twinax” cables, have gained popularity for their unique characteristics and capabilities.
A Twinaxial cable, commonly known as a “Twinax” cable, is a type of electrical cable used for transmitting data and signals.
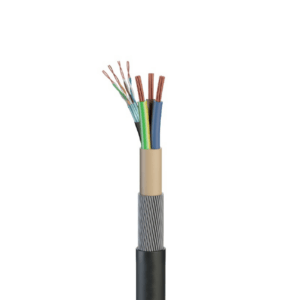
The name “Twinax” comes from its’ construction, involving two inner conductors insulated from each other and enclosed by an outer shielding.
The term “Twinaxial” is a portmanteau of “twin” and “coaxial,” reflecting the cable’s unique design.
What is the Construction of Twinaxial Cables?
- Inner Conductors – At the core of a Twinaxial cable are two conductors, usually made of copper. Two conductors twist together, similar to how Ethernet cables feature twisted pairs. The twisting helps reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk between the conductors.
- Insulation – Insulating each inner conductor individually prevents electrical contact between them. Manufacturers use various materials for this insulation, including polyethylene (PE) or foam dielectric.
- Shielding – Surrounding the insulated conductors is a metallic shielding layer, often made of braided copper or aluminium foil. This shielding provides protection against external EMI and ensures signal integrity.
- Outer Jacket – A protective jacket made of PVC or a similar material encases the cable inside. This jacket safeguards the internal components from physical damage, moisture, and environmental factors.
How do Twinaxial Cables Work?
Twinaxial cables are well-suited for high-frequency signal transmission. When an electrical signal runs through the inner conductors, the twisted design reduces the electromagnetic fields produced by the current flow. This design reduces signal loss, crosstalk, and interference, allowing for efficient data transmission, especially over relatively long distances.
Twinaxial cables frequently find use in high-speed data transfer applications like computer networking, video transmission, and connecting data storage devices.
What is the difference between Twinaxial Cables & Coaxial Cables?
Twinaxial cables share some similarities with coaxial cables, another common choice for data transmission, but they also have distinct differences:
- Structure – Coaxial cables feature a single inner conductor, enclosed by an insulator and a metallic shielding layer. Twinaxial cables, on the other hand, have two closely spaced inner conductors.
- EMI and Crosstalk – Twinaxial cables are better at minimising EMI and crosstalk because of their twisted pair configuration. Coaxial cables are also effective at this, but Twinaxial cables have an edge in certain high-frequency applications.
The following applications use Coaxial Cables:
- Broadcasting
- Cable Television
- High-frequency RF applications
Networking, Computer Connections, and data storage connections favour Twinaxial cables.
In Summary:
Twinaxial cables are a unique and effective solution for high-speed data transmission, offering low EMI and crosstalk.
Their construction, with two closely spaced conductors and shielding, sets them apart from coaxial cables.
Understanding the differences between these cable types helps you chose the most suitable option for your specific application.
Securi-Flex® offer a range of Twinaxial Cables which are available directly from stock.
If you have more questions, feel free to contact our friendly team. We’re always happy to help!