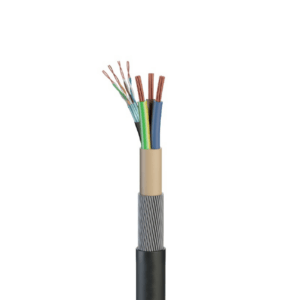
Flexible Cable, also known as, ‘continuous-flex’ is a type of cable that provides increased flexibility and durability for applications that require difficult cable placement or motion.
They are specifically engineered to withstand the tight bending radius and physical stress of moving applications.
Flex cables are be used by most of your portable electric gadgets and light pendants.
The permanent wiring that goes through the walls/ceilings between the fixture and the power source is known as “cable,” whereas the wire used to connect portable items such as lights to a wall socket is known as “flex” or “flex cable.”
Applications
Below are some of the applications in which flexible cables are used:
- Drag chain application
- Repetitive bending and torsion stress
- Machine tools
- Data processing equipment
- Robotics
- Assembly lines
- Automation networking
- Microprocessors
- Computer interconnects
Flex Power Colours
Flexible flat power cables have curved edges and include 2-4 cores. Flex (flexible cable) is circular and has 2-3 cores. The separated copper wires within the cable/flex are known as cores.
Each core (excluding the earth core in cables) is insulated with a color-coded PVC insulation that protects and enables for simple identification.
The cores are then coated in a final layer of PVC insulation known as a sheath, which is often grey or white.
- Brown – live
- Black – neutral
Is Flexible Power Cable Suitable for Outside Use?
The same principles apply to flexible cables as they do to any other type of electrical wire.
A cable must be weather resistant to be regarded suitable for outdoor use.
In general, weather resistance comprises resistance to the following elements:
- Ambient temperature.
- Ultraviolet radiation.
- Ozone.
- Water.
Even though many flex-type cables are outdoor-rated, certain flex cables cannot tolerate exterior extremes such as UV radiation.
How Long Can You Run Flex Power Cable?
There are a few aspects that should be considered when running a flexible power cables. The maximum length should not exceed:
- 12m – for flexes with 1.25mm2 conductors
- 15m – for flexes with 1.5mm2 conductors
- 25m – for flexes with 2.5mm2 conductors
However, if the extension lead is plugged into a residual current device (RCD) protected socket then 25 metres is still considered safe, but if there is no RCD the maximum length should not be more than 10 metres. That is because the most used flexes are 0.75mm or 1mm2.