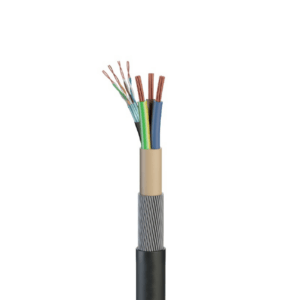
Data cables are used to transmit electronic data from one location to another. Data cabling is either copper or fibre optics, and it is widely utilised in computer and communications systems.
They can be classified into three major types:
- Coaxial cables (copper)
- Twisted pair cables (copper)
- Optic cables (fibre)
Each has distinct properties that makes them identifiable.
Coaxial
Coaxial cable carries high frequency signals, and it is mostly used in older computer networks. These types of cable have a solid wire core conductor that is enclosed in an insulator and covered by a metal foil outer conductor. The circuit is completed by this outer conductor, and the entire cable is secured by a plastic cover.
Though coaxial cables have a larger bandwidth, they have a far higher attenuation than twisted-pair cables. It’s common in digital telephone cable wiring networks, where a single cable may transmit up to 600 Mbps of data.
Coax cabling requires the use of a specific connection known as a BNC connector, which is used to connect the cable’s end to a device.
Twisted Pair

Twisted pair cables are primarily used for telecommunications and computer networks. They are made up of two copper cores that are twisted together, and each have their own plastic insulation – one carries the signal while the other is used as ground reference.
The benefit of twisting is that external factors affect both wires equally. The twisting of the wires protects data transfers from signal deterioration. However, the typical length of a twisted pair cable before signal loss is around 300 feet.
Types of Twisted Pair Cables
- UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair)
- STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) cable – has one additional metal shield covering the insulated twisted pair conductors
Fibre Optic Cable
Fibre optic cables provide fast connections to the Internet via data signals in the form of light. They are primarily used in cable and telephony companies.
The light channel consists of two major parts:
- Core
- Cladding – protective cover of the core
Fibre optic cable is lightweight, and unlike the other two data connections, it does not suffer from signal deterioration. Fibre optic cable, on the other hand, is more costly and more delicate due to the glass sections of the cable.
Types of Connectors
- SC connector – used for cable TV
- ST connector – used for connecting cable to networking devices
Different Types of Connector for Data Cables
- Registered Jack 45 (RJ45) – found in UTP & STP cables
- Straight Tip (ST) – usually found on the end of a multi-mode cable
- Subscriber Connector (SC) – found on Multimode and Single Mode optical fibre cables
- Lucent Connector (LC) – found on high-density deployments where multiple fibres would be terminated in a confined space
- Multi-fibre Push On (MPO) – duplex connector that was created with the intention of being able to be connected several times without causing any possible connection troubles
What is the Most Used Cable Type for Networking?
Unshielded Twisted Cable is the most popular and, in most cases, the best solution for LANs. In some situations, however, the Shielded Twisted Pair may be preferable.
For more information on our range of data and ethernet cables, get in touch with our expert team!