Twisted pair cabling is used for telecommunications services as well as most recent Ethernet networks. A circuit is formed by a pair of wires that may carry data. The pairs are twisted to prevent crosstalk, or noise caused by nearby pairs.
In an electrical circuit, when two wires are positioned close together their magnetic fields are opposite, which means they both cancel each other out and any outside magnetic fields. This cancelling effect is increased by twisting the wires.
There are two main types of twisted-pair cabling – unshielded twisted pair and shielded twisted pair.
UTP Cable
Unshielded twisted pair cables depend only on the cancelling effect created by twisted wire pairs to prevent signal deterioration caused by electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI).
To additionally reduce crosstalk, the numbers of twists on the wires ranges, but they must adhere to strict regulations controlling the number of twists or braids allowed per metre of cable.
Advantages
- UTP has small external diameter – it does not fill up ducts quickly
- Easy to install
- Cost-effective
- UTP can be used with most networking architectures
Disadvantages
- Prone to electrical noise
- Distance between signal boosts is shorter
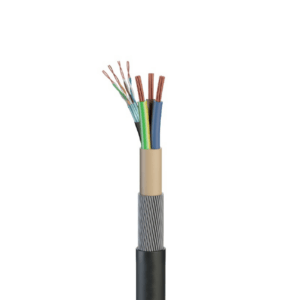
STP Cable
Shielded twisted pair wires are covered with metallic foil. The four pairs are then wrapped in metallic braid or foil for further protection. These types of cable are typically used in Ethernet network installations. They reduce electrical noise both from within (pair coupling, or crosstalk) and from outside (EMI and RFI).
Both ends of the metallic shielding must be grounded – if it is not correctly grounded, it works as an antenna, picking up undesired signals.
Advantages
- Better protection
- Faster
Disadvantages
- More costly
- Difficult to terminate
How Deep Should Communications Wire be Buried?
The ducting for telecom cables should be buried at a 250mm minimum to the premises and it should be as straight as possible.
Non-armoured cables, such as UTP, should always be run inside a protective conduit or a duct. Armoured cables, such as STP, could be buried on their own if they have a steel outer coating.
Other Types of Telecom Cables
The two other types of telecommunication cables that are mainly used are coaxial and fibre optic cables.
Coax cables are used for:
- Internet connection
- Transmitting cable TV signals
- Connecting radio transmitters to receivers
Fibre optic cables are used for:
- Internet connection
- Computer networking
- Medicine and research
And many more advanced technologies such as military and space applications. Find a wholesaler today to shop our range of telecom cables!